SPECIFICATION GENERATOR
Find out which low impact materials are right for your building project.
Psi Values, Thermal Bridging And Wood Fibre Insulation
Find out more about how we approach this building scenario.
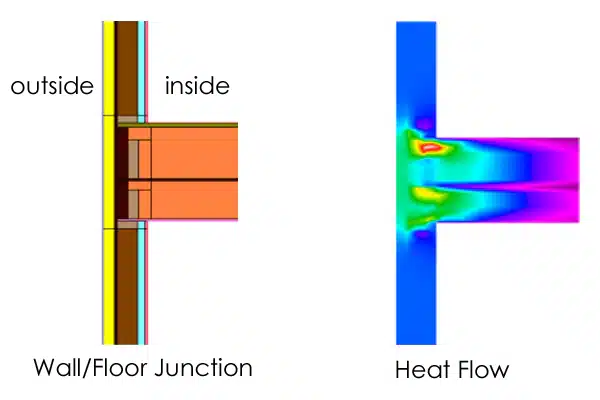
Psi values (pronounced p’see) are a measurement of the heat loss that occurs at all junctions where non-repeating thermal bridges occur. These can be wall to wall junctions, wall to ground floor/suspended floor, wall to roof, wall to window/door junctions and also in party wall/floor junctions.
Calculation of these values is generally done using software, such as THERM, and is entirely dependent on the design of the junction. Whenever you change the materials or the design of the junction the Psi value will change. Therefore, whilst you can give the typical Psi values for a system, if there is any variation from the default design then there should be a re-calculation.
Once all of your Psi values are calculated, they are multiplied up by the length of each junction to give an overall y-value. The y-value is then divided by the total heat loss area and is then input into your SAP software.
The myth of ‘high performance insulation’
The wood fibre insulation systems we provide are well detailed, minimise thermal bridges across all junctions and give inherently low psi values. So much so that using synthetic materials with lower conductivities does not always create a design with an overall lower U-value once the Psi values are included. Although the insulation material may have a lower conductivity if it allows many repeat and non-repeat thermal bridges it will be less effective than another insulation system that does not.
For our externally rendered and clad timber frame solutions, typical Psi values for a 140mm timber frame are as follows:-
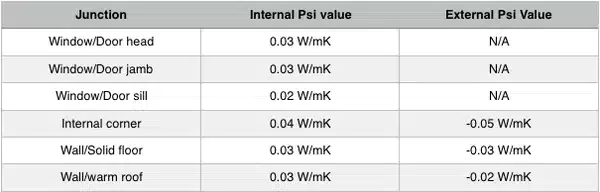
The above table shows some values for internal and external Psi values. This is to accommodate the difference between methodologies in heat loss assessment between SAP and PHPP (the tool used for assessment of Passivhaus designs). SAP, optimistically, uses the internal surface areas to calculate heat loss. PHPP, realistically, uses the external surface areas to calculate heat loss.
If you have any questions about Psi values and how they affect your building, please contact us.
